Introduction
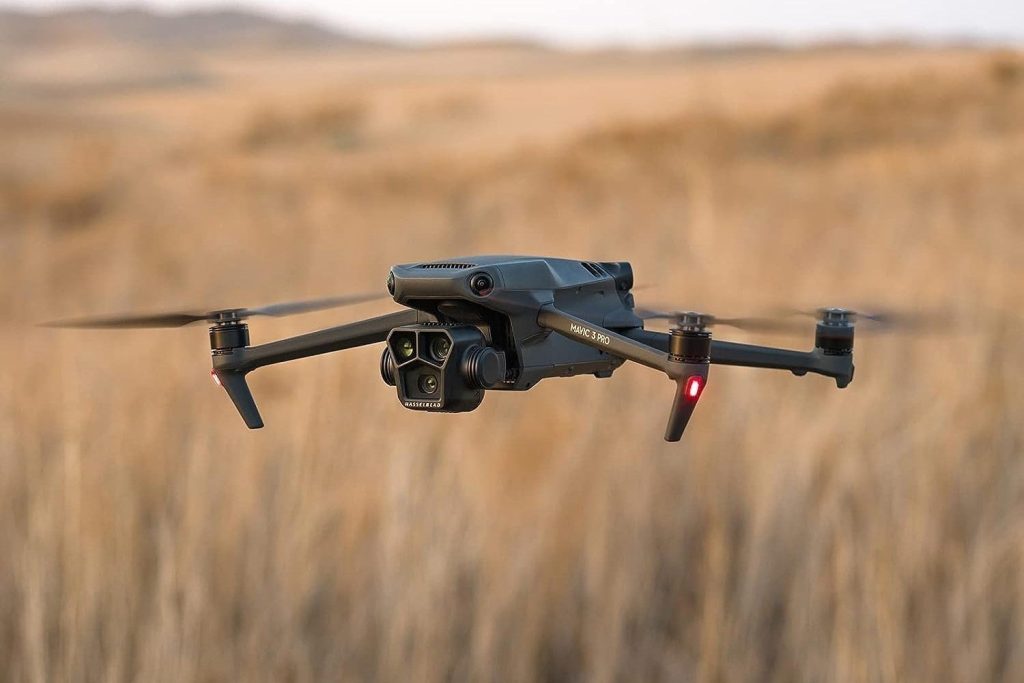
In recent years, drones have evolved far beyond their initial role as recreational gadgets or tools for aerial photography. With rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and computer vision, drones are now becoming a key component of industrial automation. In 2025, autonomous drones are transforming industries such as manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, and infrastructure management by performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention. This shift represents a major milestone in the journey toward smarter, more efficient, and data-driven industrial operations.
Table of Contents
Understanding Autonomous Drones
An autonomous drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) equipped with advanced sensors, onboard computing systems, and AI-driven algorithms that allow it to navigate and perform tasks without direct human control. Unlike manually operated drones, autonomous drones can plan flight paths, avoid obstacles, and adapt to environmental conditions in real time. They rely on a combination of GPS, LiDAR, computer vision, and machine learning models to understand and interact with their surroundings.
These drones are part of a larger technological ecosystem that includes the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, and cloud analytics. They collect data from various sensors, process it locally or in the cloud, and execute intelligent actions based on analysis. This integration enables industries to automate inspection, monitoring, and delivery processes more effectively than ever before.
Applications in Industrial Sectors
The impact of autonomous drones spans across multiple industries. In logistics and supply chain management, drones are revolutionizing how goods are moved and monitored. Companies like Amazon and UPS are testing autonomous delivery systems that use drones to transport small packages directly to customers. In large warehouses, drones equipped with scanning technology perform inventory checks faster and more accurately than human workers.
In construction and infrastructure, drones are being used for site mapping, progress tracking, and safety inspections. High-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors allow them to create detailed 3D models of construction sites, helping engineers make data-driven decisions. These drones can also detect structural defects in bridges, pipelines, and power lines, reducing the need for risky manual inspections.
In agriculture, autonomous drones are enhancing precision farming by monitoring crop health, assessing soil quality, and even performing targeted pesticide spraying. Farmers can analyze aerial data to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer application, and harvesting schedules. This not only boosts productivity but also minimizes resource waste.
In energy and mining, drones are used for monitoring remote assets such as wind turbines, solar farms, and mining sites. They can detect leaks, corrosion, or malfunctions quickly, improving maintenance efficiency and reducing downtime. These industries benefit greatly from drones’ ability to operate in hazardous or hard-to-reach environments where human safety is at risk.
Advantages of Autonomous Drones in Automation
The integration of autonomous drones into industrial workflows brings numerous benefits. Efficiency is one of the most significant advantages. Drones can perform repetitive and time-consuming tasks around the clock, reducing operational costs and human labor requirements.
Another key advantage is accuracy. With sophisticated sensors and AI-driven analytics, drones can capture precise data that improves decision-making and quality control. In industries where safety is critical, such as oil and gas or construction, drones also provide risk reduction by performing dangerous inspections in place of human workers.
Speed and scalability further enhance industrial automation. Drones can rapidly cover vast areas and handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making them ideal for large-scale operations. Additionally, their ability to integrate with existing management systems allows seamless coordination with other automated technologies such as robots, sensors, and AI software.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their growing adoption, autonomous drones face several challenges. One of the main barriers is regulatory compliance. Many countries still lack comprehensive frameworks governing autonomous flight operations, especially in populated or restricted areas. Obtaining permissions for beyond-visual-line-of-sight (BVLOS) operations remains difficult.
Battery life and payload capacity are also technical limitations. Current drones can typically operate for limited durations before needing to recharge, which restricts their range and productivity. Researchers are working on improved energy storage solutions and hybrid power systems to extend flight times.
Data security and privacy are additional concerns. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can inadvertently capture sensitive information, raising ethical and legal issues. Companies must implement strong data protection policies and encryption standards to safeguard collected information.
Finally, environmental conditions such as wind, rain, and extreme temperatures can affect drone performance. Designing drones that can adapt to different climates remains an ongoing engineering challenge.
The Future of Autonomous Drones in Industry
The future of industrial automation will heavily rely on drone technology. As AI models become more powerful and battery technology advances, drones will gain greater autonomy and endurance. Integration with 5G networks will enable real-time communication between drones and control centers, improving coordination and responsiveness.
In the coming years, we can expect fully autonomous drone fleets that work collaboratively with ground robots and AI systems to manage industrial operations end to end. Predictive analytics will allow drones to anticipate issues before they occur, shifting industries from reactive to proactive management.
Governments and private sectors are also likely to invest in developing drone corridors — dedicated aerial routes for commercial drones — to streamline autonomous operations and ensure airspace safety. This evolution will make drones a permanent fixture in industrial ecosystems.
Conclusion
Autonomous drones are revolutionizing industrial automation by enhancing efficiency, safety, and data accuracy across multiple sectors. As 2025 unfolds, their role will expand from supportive tools to integral components of intelligent industrial networks. The combination of AI, robotics, and connectivity is driving industries toward a future where machines can operate independently and intelligently. The rise of autonomous drones signifies not just a technological advancement but a complete redefinition of how industries function in the digital era. Also Check Satellite Internet – Powering Internet – Ultimate Guide 2025






1 thought on “Rise of Autonomous Drones in Industrial Automation – 2025”